Australia’s New Sand Battery Stores Solar Power for Days – Even Without Sunshine!
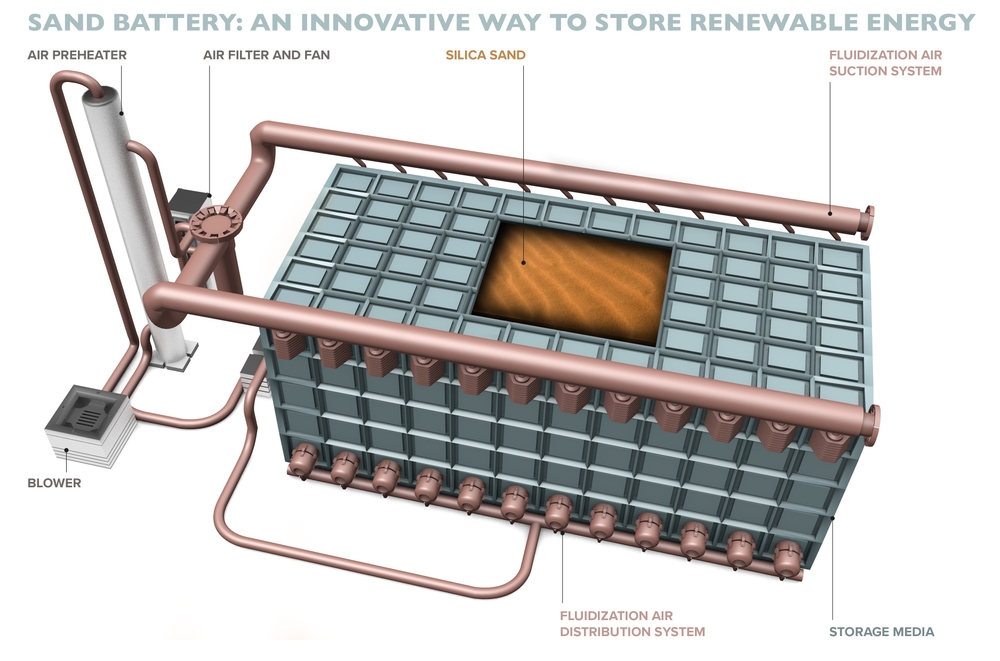
Imagine a world where the sun’s energy could be stored for days, not hours, even when the sun isn’t shining. What if the secret to unlocking clean energy for the long term didn’t lie in rare metals or complicated technology, but in something as simple as sand? This is no longer a distant dream—it’s a reality that’s unfolding in Australia.
In the midst of a global push for sustainable energy solutions, scientists have found a groundbreaking way to store solar power—using sand. This simple, abundant material could revolutionize how we think about energy storage, offering a solution to one of the most significant hurdles in the clean energy revolution: how to store solar power when the sun isn’t shining.
What is a Sand Battery?
A sand battery represents a revolutionary leap in energy storage technology, using the abundant material of sand, particularly the silicon derived from it, to store and release solar energy. Unlike traditional energy storage systems that rely on complex chemical processes, sand batteries store energy as heat, using the unique properties of silicon to absorb and retain this thermal energy. Silicon is heated to high temperatures—often exceeding 1,000 degrees Celsius—and can store energy for extended periods, making it available even when the sun isn’t shining. When this energy is needed, it’s released as electricity, making the entire process efficient and scalable.
One of the standout features of sand batteries is their simplicity and environmental friendliness. While other forms of energy storage rely on precious or rare materials, sand is widely available and requires little to no processing to be used effectively.
The extraction of silicon from sand is straightforward, and because it doesn’t require rare earth metals or complicated manufacturing processes, the cost is significantly lower than that of other battery technologies, such as lithium-ion batteries. In a world where the demand for clean and affordable energy solutions is rapidly growing, sand batteries offer a practical, low-cost, and sustainable alternative to existing methods.
Another benefit of sand batteries is their long-term viability. Traditional energy storage systems, like lithium-ion batteries, often degrade over time and lose their ability to hold a charge. Sand, however, is a stable and resilient material, meaning that sand batteries have the potential to last longer without losing efficiency. This longevity is essential for creating a future energy system that doesn’t just rely on renewable sources like solar and wind but also ensures that the energy we collect can be stored and used reliably, even in areas where energy demand peaks after the sun sets or during periods of cloudy weather.
How Sand Batteries Solve Energy Storage Problems

The challenge of energy storage has always been a significant barrier to the widespread use of renewable energy sources. Solar and wind power are intermittent—they rely on the sun shining and the wind blowing, respectively—and this intermittency makes it difficult to store energy for later use. Traditional methods of energy storage, such as lithium-ion batteries, have proven useful but come with limitations. Lithium-ion batteries are expensive, require rare minerals, and degrade over time, making them less than ideal for long-term, large-scale energy storage. Sand batteries, however, promise to solve many of these issues by offering a cheaper, longer-lasting, and more environmentally friendly solution.
What sets sand batteries apart is their ability to store solar energy for days, not just hours. Traditional batteries typically store energy for short periods—generally just enough to cover the gap between daytime energy production and nighttime use. However, the sand battery’s ability to store thermal energy for extended periods—days, even weeks—opens up entirely new possibilities. This capability is critical for integrating solar power into existing energy grids, where energy demand often spikes during non-sunny hours. The ability to store energy for extended periods also makes sand batteries ideal for areas with inconsistent sunlight or those that experience long periods of darkness, such as regions far from the equator or in more temperate climates.
Another major advantage of sand batteries is their potential to lower the cost of energy storage significantly. While lithium-ion batteries can be prohibitively expensive due to the high cost of raw materials like lithium and cobalt, sand is inexpensive and abundant. As a result, sand batteries could help reduce the overall cost of renewable energy systems, making them more accessible to individuals, businesses, and governments worldwide. The affordability of sand batteries is particularly appealing for communities that are off the grid or in remote locations, where traditional energy infrastructure is either nonexistent or too costly to implement.
The Australian Sand Battery Breakthrough

In Australia, a team of researchers has taken the concept of sand batteries from theoretical to practical, demonstrating that it is possible to store solar energy for days using this novel technology. Their breakthrough has shown that sand can serve as an efficient and cost-effective medium for storing energy, allowing solar power to be stored and used long after the sun has set. The prototype developed in Australia uses sand that is heated to extreme temperatures during the day, storing thermal energy that can then be converted back into electricity when needed. This has significant implications for the renewable energy sector, as it could pave the way for a much more sustainable and reliable energy storage solution.
The success of this sand battery project is particularly impactful for Australia, a country that is blessed with abundant sunlight but also faces challenges related to energy storage in its vast, sparsely populated regions. The ability to store energy in sand for days would solve many of the logistical and financial challenges of renewable energy in remote communities, where access to the grid can be limited or nonexistent. By creating an efficient, low-cost method of energy storage, the sand battery has the potential to bring reliable, affordable solar power to areas that are traditionally dependent on fossil fuels or costly, unreliable energy sources. This breakthrough could also reduce the nation’s reliance on imported energy, helping Australia become more self-sufficient in its energy needs.
Moreover, this Australian development is just the beginning. The potential applications of sand batteries go far beyond the immediate needs of Australia. As the technology continues to evolve, it could be scaled up for use in solar farms, homes, and industries around the world. Researchers and governments are already looking at ways to expand on this initial success, improving the efficiency of sand batteries and making them even more effective for large-scale energy storage. In a world where the transition to clean energy is a global priority, Australia’s success with sand batteries offers hope for a more sustainable and reliable energy future, not just for Australia, but for the entire planet.
Why This Is a Game-Changer for Clean Energy

The sand battery represents a pivotal moment in the evolution of clean energy storage. For years, the energy sector has faced the challenge of finding a reliable and affordable way to store the massive amounts of energy generated by renewable sources like solar and wind. While lithium-ion batteries have been the go-to solution, they are far from perfect. They are expensive, have limited lifespan, and rely on minerals that are difficult to obtain sustainably. Sand batteries, on the other hand, offer a more sustainable, affordable, and long-lasting solution to these problems. The environmental impact of sand, coupled with its availability, makes it an incredibly attractive option for clean energy storage, especially when compared to the rare and toxic materials used in traditional batteries.
Not only is the sand battery environmentally friendly, but it also offers a much-needed improvement in terms of energy storage capacity. The ability to store solar energy for extended periods—days or even longer—could solve one of the most significant challenges of renewable energy: intermittency. In regions where solar power generation is seasonal or inconsistent, sand batteries could ensure that the energy generated during sunny days could be used during the night or even on cloudy days. This ability to store energy over a long period could revolutionize how we think about energy storage, making solar power not just a daytime energy source, but a round-the-clock solution.
The broader implications for global energy systems are immense. If sand batteries can be scaled up and deployed at a larger scale, they could provide a reliable and cost-effective way to store energy in regions around the world, particularly those that struggle with energy access or have limited infrastructure. The low cost of sand, combined with its widespread availability, could make energy storage more accessible to communities that have traditionally been excluded from the renewable energy revolution. This breakthrough could help ensure that clean, renewable energy is not just an ideal, but a practical, accessible solution for people everywhere.
The Road Ahead: Scaling Up and Potential Challenges

While the concept of sand batteries is undeniably promising, there are still significant challenges to overcome before they can be fully scaled and implemented on a global level. The most immediate challenge is improving the efficiency of the technology. While sand batteries have proven to be effective in storing energy for several days, researchers are still working on increasing their energy storage capacity and efficiency. The current prototypes show great potential, but there is room for improvement in terms of how much energy can be stored, how quickly it can be retrieved, and how much energy is lost in the process.
Another challenge lies in the infrastructure needed to support sand battery systems. While the technology itself may be relatively simple, the large-scale implementation of sand batteries would require significant investment in new infrastructure, such as thermal storage facilities and energy distribution networks. Governments and businesses would need to collaborate to build this infrastructure, ensuring that sand batteries can be deployed effectively in both urban and rural areas. The cost of scaling up the technology may be high, but the long-term savings could be substantial, especially considering the low cost of the materials involved.
Despite these challenges, the potential benefits of sand batteries make them an exciting prospect for the future of renewable energy. As research continues and the technology improves, it’s possible that sand batteries could become a cornerstone of global energy systems, helping to address the energy storage challenges that have long hindered the widespread adoption of renewable energy sources. With the right investments and support, sand batteries could play a crucial role in creating a cleaner, more sustainable, and energy-efficient future.
Finding Power in Unexpected Places

Life has a way of throwing challenges at us, but just like the breakthrough with sand batteries, we have an incredible ability to adapt and bounce back. Think about it—this technology is changing the way we store energy, using something as simple and abundant as sand. And that’s a powerful reminder of how, as individuals, we too can find solutions in unexpected places when we’re open to change and innovation.
Just like the scientists who saw potential in sand, we all have moments when we face obstacles that seem bigger than we are. But if we approach life with the same creativity and adaptability, we can overcome anything. It’s about being willing to try new things, learning from our mistakes, and not being afraid to think outside the box. Whether it’s making a tough decision in our personal lives or finding a healthier way to manage stress, embracing innovation means being open to doing things differently.
Innovation isn’t just about new gadgets or technology; it’s about how we approach our lives. Just as a sand battery can store energy for days, we can build up resilience and wisdom over time, using our experiences to guide us when things get tough. The key is to take charge of our own journey, stay curious, and keep evolving. Because in the end, it’s our willingness to adapt and innovate that helps us grow, not just as individuals, but as a part of a bigger, changing world.
A New Era for Renewable Energy

The advent of sand battery technology represents a profound shift in how we approach energy storage and renewable energy. By using an abundant, inexpensive material like sand, this technology offers an affordable and sustainable solution to the energy storage challenges that have long plagued solar and wind energy. The success of sand batteries in Australia is just the beginning, and as the technology continues to develop, it has the potential to revolutionize how we store and use energy, making renewable energy more reliable, accessible, and cost-effective than ever before.
The potential for sand batteries is not just about technology; it’s about changing the way we think about energy. By relying on simple, renewable resources and cutting-edge science, sand batteries could help create a future where clean energy is not just a lofty goal, but a reality for people everywhere. With further research and global collaboration, the sand battery could become the cornerstone of a new, sustainable energy era—one where our energy needs are met without compromising the planet’s health or future.
Featured Image Source: Shutterstock
Loading...

